TIG Argon Welding
$5500.00
TIG Argon Welding (GTAW) Professional Training: 5-Day Advanced Certification Course
Course Overview
This comprehensive 5-day TIG welding course provides intensive hands-on training in Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) techniques designed for precision applications across Saudi Arabia (KSA), Oman, UAE, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, and African industrial markets. This advanced TIG welding certification program covers tungsten electrode technology, inert gas shielding, pulse welding, all-position techniques, and multi-metal capability essential for aerospace manufacturing, pharmaceutical equipment, food processing, petrochemical piping, power generation, and high-quality fabrication throughout the GCC region and Africa.
Target Audience
Precision welders in Saudi aerospace facilities and GCC pharmaceutical manufacturing
Pipe welders requiring ASME Section IX TIG certification for oil and gas industries
Stainless steel fabricators in food processing and dairy industries across Middle East
Maintenance technicians in power plants, refineries, and chemical facilities
Aluminum welders for automotive, marine, and architectural applications in UAE
Quality-focused professionals seeking premium welding skills for specialized African industries
Day 1: TIG Welding Fundamentals and Equipment Technology
Morning Session: Introduction to GTAW Process
TIG welding principles: non-consumable tungsten electrode, separate filler metal addition
Process advantages: superior weld quality, precise heat control, minimal spatter, clean welds
Applications: stainless steel piping (Saudi Aramco), aluminum aerospace components (UAE)
Material versatility: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, copper, nickel alloys
Industry requirements: ASME B31.3 process piping, API 650 storage tanks, EEMUA 234 standards
Career opportunities: premium salaries (SAR 8,000-20,000) for certified TIG welders in GCC
GTAW vs other processes: quality comparison, cost-benefit analysis for critical applications
Afternoon Session: TIG Welding Equipment Components
Power source types: transformer machines, inverter technology, AC/DC capabilities
Constant current (CC) characteristics: stable arc, precise amperage control
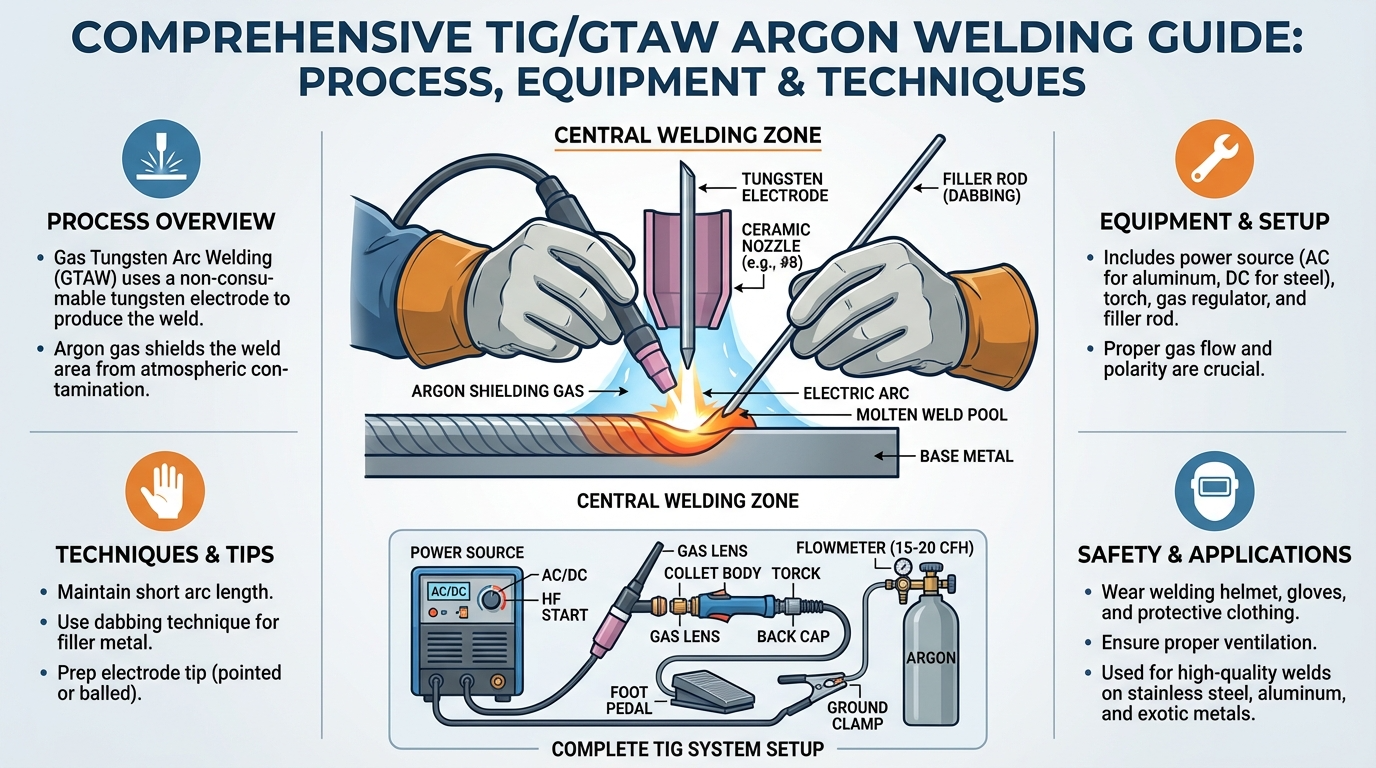
TIG torch components: torch body, collet, collet body, ceramic cup, gas lens
Air-cooled vs water-cooled torches: amperage capacity (200A vs 500A+) selection
Tungsten electrodes classification: pure, 2% thoriated, 2% ceriated, 2% lanthanated
Electrode grinding techniques: proper taper angles, contamination prevention
Shielding gas systems: Argon purity (99.99%), Helium, Argon-Helium mixtures
Gas flow rates optimization: 10-20 CFH for standard applications, trailing shields
Foot pedal amperage control: remote current adjustment during welding
High-frequency start: contactless arc initiation preventing tungsten contamination
Equipment setup practice: torch assembly, tungsten preparation, gas connection verification
Safety protocols: proper ventilation, fume extraction for stainless steel hexavalent chromium
Learning Outcomes: Complete understanding of precision TIG welding technology and equipment operation essential for high-quality welding positions in GCC aerospace and African specialty manufacturing.
Day 2: DC TIG Welding - Steel and Stainless Steel Applications
Morning Session: DC TIG Welding Fundamentals
DCEN (electrode negative) polarity: standard configuration for steel and stainless
Arc characteristics: concentrated heat, deep penetration, stable arc control
Tungsten selection: 2% ceriated (red), 2% lanthanated (blue) for DC applications
Electrode diameter selection: 1.6mm, 2.4mm, 3.2mm based on amperage requirements
Filler metal selection: ER70S-2 (mild steel), ER308L, ER316L (stainless steel)
Filler rod sizes: 1.6mm, 2.4mm, 3.2mm matching base metal thickness
Cup size selection: #4-#8 ceramic cups for different joint accessibility
Gas lens benefits: laminar gas flow, improved shielding coverage, extended stick-out
Afternoon Session: Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel Flat Position Welding
Joint preparation: edge beveling, root gap, tack welding techniques
Arc starting procedures: high-frequency vs scratch start methods
Torch angle optimization: 70-80° work angle, 10-15° travel angle
Filler metal addition: dabbing technique, maintaining arc length consistency
Puddle control: watching weld pool, adjusting travel speed for penetration
Walking the cup technique: torch stabilization for consistent bead appearance
Stringer beads practice: running continuous beads on mild steel and stainless steel
Butt joint welding (1G): root pass, fill passes, cap pass sequences
Fillet welds (1F): T-joints for stainless steel tanks and pharmaceutical vessels
Stainless steel considerations: lower heat input, preventing carbide precipitation
Corrosion resistance: L-grade stainless (308L, 316L) for food processing equipment
Extensive hands-on practice: 50+ beads developing muscle memory and coordination
Applications: petrochemical piping (SABIC), desalination plants (GCC), dairy equipment (Africa)
Learning Outcomes: Proficiency in DC TIG welding on ferrous metals suitable for precision piping, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and food processing industries across GCC and African markets.
Day 3: AC TIG Welding - Aluminum and Advanced Techniques
Morning Session: AC TIG Welding Fundamentals
Alternating current principles: electrode negative cycle (penetration), positive cycle (cleaning)
Cleaning action importance: oxide layer removal on aluminum and magnesium
Balance control: adjusting EN/EP ratio (typically 70% EN, 30% EP)
Frequency adjustment: higher frequency (100-200Hz) for focused arc, smoother operation
Tungsten selection: pure tungsten (green) or zirconiated (white) for AC welding
Balled tungsten end: proper electrode preparation for AC applications
Power source requirements: AC/DC machines with square wave technology advantages
Afternoon Session: Aluminum TIG Welding Practice
Aluminum alloy classifications: 1xxx, 3xxx, 5xxx, 6xxx series properties and weldability
Filler metal selection: ER4043 (silicon), ER5356 (magnesium) for different applications
Surface preparation critical: stainless steel brush, acetone cleaning, oxide removal
Preheating requirements: 150-200°F for thick sections (>6mm) preventing porosity
Amperage requirements: approximately 1 amp per 0.001" material thickness guideline
Puddle characteristics: recognizing proper fusion, fluidity indicators
Porosity prevention: proper gas coverage, cleaning procedures, avoiding hydrogen sources
Black soot removal: post-weld cleaning for aesthetic appearance
Flat position aluminum welding: butt joints, lap joints, fillet welds practice
Applications: automotive components (Saudi automotive industry), architectural panels (UAE)
Marine applications: aluminum boat fabrication (African fishing industry), yacht building (GCC)
Heat sink effects: aluminum’s high thermal conductivity welding challenges
Hands-on exercises: extensive practice on 3mm-6mm aluminum plates and extrusions
Learning Outcomes: AC TIG welding mastery enabling aluminum fabrication careers in GCC aerospace, automotive, architectural, and African marine industries commanding premium salaries.
Day 4: All-Position TIG Welding and Pipe Welding Fundamentals
Morning Session: Horizontal and Vertical Position TIG Welding
Horizontal groove welds (2G): gravity management, filler metal control techniques
Torch angle adjustment: slightly upward angle preventing sag on vertical surface
Vertical-up TIG welding (3G): keyhole technique for root pass penetration
Stairstepping method: building weld vertically with controlled filler addition
Heat management: preventing burn-through while maintaining proper fusion
Vertical stainless steel applications: pharmaceutical reactor vessels, chemical process tanks
Pulsing amperage benefits: better puddle control in vertical/overhead positions
Practical exercises: 2G and 3G qualification test preparation on stainless steel
Afternoon Session: TIG Pipe Welding Introduction
Orbital position importance: 80% of pipe welding in oil and gas infrastructure
Pipe joint preparation: 37.5° bevel angle, 1/16" root gap, 1/16" land thickness
Root pass critical techniques: open root keyhole method, consistent penetration
Fixed pipe (5G) position: 12 o’clock to 6 o’clock welding progression
Filler metal manipulation: feeding rod consistently into leading edge of puddle
Hot pass requirements: fusing root pass, slight reinforcement building
Fill and cap passes: building proper reinforcement height, smooth transitions
Walking the cup on pipe: stabilization technique for consistent bead profile
ASME Section IX qualification: 6G position test for all-position certification
API 1104 requirements: pipeline construction welding standards for GCC projects
Argon backing gas: preventing root oxidation, ensuring internal weld quality
Hands-on practice: 5G position TIG welding on 2-inch schedule 40 stainless steel pipe
Career applications: Saudi Aramco piping projects, ADNOC refinery maintenance, African gas pipelines
Learning Outcomes: All-position TIG capability and pipe welding fundamentals qualifying for high-demand positions in GCC petrochemical facilities and African energy sector infrastructure.
Day 5: Pulse TIG, Exotic Metals and Certification Testing
Morning Session: Advanced Pulse TIG Welding Technology
Pulse welding benefits: reduced heat input, minimized distortion, improved puddle control
Peak current settings: achieving proper penetration during pulse peak
Background current: maintaining arc stability, reducing overall heat input
Pulse frequency optimization: 0.5-10 pulses per second for different applications
Duty cycle adjustment: percentage of time at peak current vs background
Thin material advantages: 0.5mm-1.5mm stainless steel and aluminum without burn-through
Automotive exhaust systems: precision TIG welding for performance vehicles
Aerospace applications: titanium and Inconel welding for UAE aerospace industry
Practical demonstrations: pulse TIG on thin gauge stainless steel and aluminum
Afternoon Session: Exotic Metals and Qualification Testing
Titanium welding fundamentals: inert gas trailing shields, chamber welding requirements
Nickel alloys: Inconel 625, Hastelloy for chemical processing equipment
Copper and copper alloys: high thermal conductivity challenges, preheating requirements
Dissimilar metal joining: stainless to carbon steel, aluminum to steel techniques
AWS D17.1 aerospace welding specification: stringent requirements for aircraft components
ASME Section IX performance qualification test: test coupon preparation and execution
Bend test procedures: root bend, face bend specimen evaluation
Radiographic examination: understanding RT acceptance criteria for TIG welds
Visual inspection standards: measuring reinforcement, undercut, surface irregularities
Qualification documentation: welder performance qualification (WPQ) record maintenance
Mock certification test: simulated 6G pipe test or 3G plate test execution
Career pathways analysis: welding inspector, welding supervisor, welding engineer progression
Salary benchmarks: experienced TIG welders (SAR 12,000-25,000) in GCC specialty industries
Job placement assistance: connections with aerospace companies, pharmaceutical manufacturers
Entrepreneurship opportunities: mobile TIG welding services for African medical equipment repair
Final practical assessment and industry-recognized TIG welding certification award
Learning Outcomes: Master-level TIG welding competency with exotic metal capabilities and certification qualifying for elite positions in GCC aerospace, pharmaceutical, and African specialized manufacturing sectors.
Course Benefits for GCC and African Markets
✓ 75% hands-on welding time on aerospace-grade equipment matching international standards
✓ Multi-metal proficiency: steel, stainless steel, aluminum, titanium welding capability
✓ ASME Section IX test preparation for immediate employment in GCC oil and gas sector
✓ Pulse TIG technology training for cutting-edge manufacturing applications
✓ Small class sizes (maximum 6 students) ensuring personalized instruction and practice time
✓ Bilingual technical training (English/Arabic) for Middle East professional accessibility
✓ Premium career positioning: access to highest-paid welding positions in GCC markets
✓ International certification: globally recognized credentials for worldwide employment mobility
Investment in Precision Welding Excellence
TIG argon welding represents the pinnacle of welding craftsmanship, commanding the highest salaries and most prestigious positions across Saudi Arabia’s aerospace initiatives, UAE’s advanced manufacturing, Oman’s LNG facilities, and Africa’s pharmaceutical expansion. With Vision 2030 technology localization, GCC industrial diversification, and African manufacturing growth, demand for certified TIG welders continues outpacing supply. Elite employers including Saudi Aerospace Engineering Industries, Stainless Steel Industries (SSI), SABIC, Ma’aden, international pharmaceutical companies, and African medical equipment manufacturers actively recruit skilled TIG welders offering competitive salaries (SAR 10,000-25,000+), international assignments, and excellent career progression.
Enroll today to master the most prestigious welding technology and access premium career opportunities in GCC specialized industries and Africa’s emerging high-tech manufacturing sector!
Keywords: TIG welding course KSA, GTAW training Saudi Arabia, argon welding certification Oman, TIG welder jobs GCC, gas tungsten arc welding UAE, aluminum TIG welding Africa, stainless steel welding course Middle East, pipe TIG welding certification Gulf, aerospace welding training, ASME Section IX TIG qualification, pharmaceutical welding GCC, precision welding course Qatar Kuwait, pulse TIG welding training, Saudi Aramco TIG welder, SABIC welding jobs, titanium welding course, TIG certification Bahrain, advanced welding training Africa


