Arc Stick Welding
$5500.00
Arc Stick Welding (SMAW) Professional Training: 5-Day Intensive Certification Course
Course Overview
This comprehensive 5-day arc stick welding course provides intensive hands-on training in Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) techniques tailored for industrial applications across Saudi Arabia (KSA), Oman, UAE, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, and African markets. This practical welding certification program covers electrode selection, all-position welding, pipe welding fundamentals, and AWS qualification standards essential for construction, oil and gas, structural steel fabrication, shipbuilding, and maintenance operations throughout the GCC region and Africa.
Target Audience
Entry-level welders seeking SMAW certification in KSA and GCC countries
Maintenance technicians in Saudi Aramco, ADNOC, and African industrial facilities
Construction workers transitioning to certified welding positions in Oman and UAE
Fabrication shop personnel requiring multi-position welding skills across Middle East
Pipeline welders preparing for API 1104 qualification in GCC and African projects
Military and vocational students pursuing welding careers in emerging African economies
Day 1: SMAW Equipment, Safety and Welding Fundamentals
Morning Session: Introduction to Arc Stick Welding
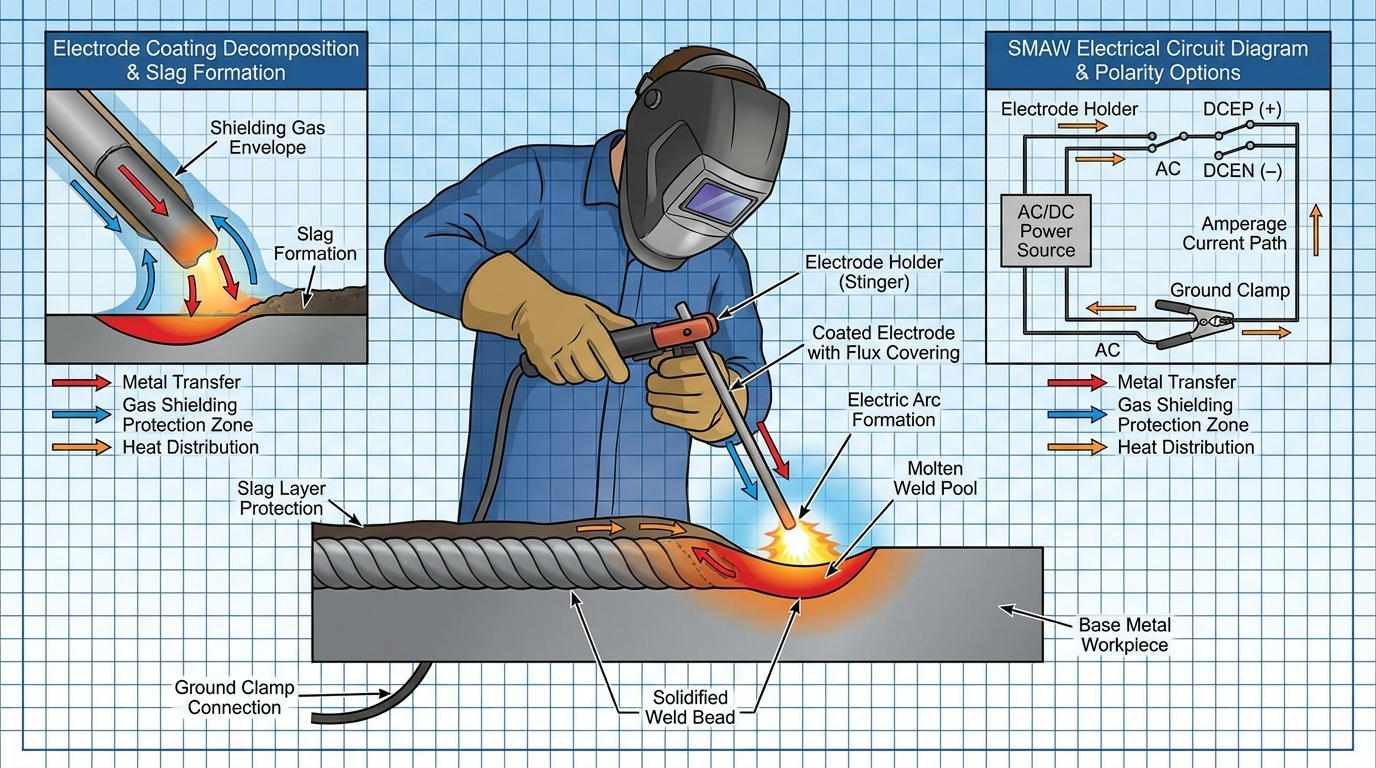
History and advantages of SMAW in field welding applications across GCC
Arc welding principles: electrical circuit, arc characteristics, heat generation
Equipment components: transformer welders, inverter machines, rectifier systems
Duty cycle ratings and machine capacity selection for different applications
Power source comparison: AC vs DC welding for various electrodes and materials
Polarity effects: DCEP, DCEN, AC applications for different electrode types
Portable welding machines for remote African construction sites and desert operations
Cost-effectiveness of SMAW for small-scale workshops in developing markets
Afternoon Session: Workplace Safety and Personal Protection
Electrical safety protocols: proper grounding, cable inspection, shock prevention
Arc radiation hazards: UV protection, proper shade selection (#10-#14 lenses)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): welding helmets, leather gloves, protective clothing
Fire prevention measures for Saudi construction sites and African workshops
Fume extraction systems and respiratory protection requirements
Confined space welding safety in tanks and pressure vessels
Hot work permits and safety procedures per KSA labor regulations
First aid for welding injuries: burns, arc flash, electric shock treatment
OSHA compliance and GCC occupational health standards
Hands-on practice: equipment setup, electrode holder connection, ground clamp positioning
Learning Outcomes: Complete understanding of SMAW equipment operation and comprehensive safety knowledge for accident-free welding in GCC and African industrial environments.
Day 2: Electrode Classification and Flat Position Welding
Morning Session: Welding Electrode Technology
AWS A5.1 electrode classification system: E6010, E6011, E6013, E7018, E7024
Electrode numbering interpretation: tensile strength, welding position, coating type
Coating types and functions: cellulose, rutile, low-hydrogen, iron powder
E6010 applications: deep penetration for pipeline root passes and open root joints
E6011 characteristics: AC capability for farm equipment repair and maintenance welding
E6013 features: smooth arc, light slag for sheet metal fabrication and general purpose
E7018 low-hydrogen electrodes: structural steel welding meeting AWS D1.1 requirements
Electrode storage requirements: rod ovens, moisture control for low-hydrogen electrodes
Amperage selection charts for different electrode sizes and material thickness
Afternoon Session: Flat Position (1G/1F) Welding Practice
Workpiece preparation: edge preparation, fit-up, tack welding techniques
Arc striking methods: scratching vs tapping technique for stable arc initiation
Arc length control: maintaining proper electrode-to-work distance (electrode diameter)
Travel speed optimization: avoiding excessive heat input and distortion
Bead appearance criteria: uniform width, consistent ripples, proper tie-in
Stringer beads vs weave beads: application and technique differences
Multi-pass welding procedures: root, fill, and cap pass sequences
Practical exercises: running continuous beads on mild steel plates (6mm-12mm)
Defect identification: porosity, undercut, overlap, slag inclusion recognition
Quality assessment: visual inspection per ASME Section IX acceptance criteria
Learning Outcomes: Proficiency in electrode selection and flat position welding techniques forming the foundation for advanced positional welding in GCC fabrication shops.
Day 3: Horizontal and Vertical Position Welding Techniques
Morning Session: Horizontal Position (2G/2F) Welding
Joint configurations: butt joints, fillet joints, lap joints in horizontal orientation
Electrode angle techniques: work angle (0-15°) and travel angle (10-15°)
Gravity effects management: preventing sag and overlap on horizontal surfaces
Current adjustment for horizontal welding: typically 5-10% reduction from flat position
Multi-pass horizontal groove welding: shelf technique for thick plate applications
Horizontal fillet welds: building proper leg size for structural steel connections
Applications: I-beams, box columns, pressure vessel circumferential seams
Hands-on practice: 2G butt joint qualification on 10mm carbon steel plates
Inspection techniques: fillet weld gauges, visual examination standards
Afternoon Session: Vertical Position (3G/3F) Welding
Vertical-up vs vertical-down welding: technique selection criteria
E6010/E6011 vertical-down: high-speed travel for sheet metal and pipe hot passes
E7018 vertical-up technique: weaving patterns (triangular, Z-weave, C-weave)
Keyhole method for vertical-up root passes in groove welds
Electrode manipulation: pausing at toes, quick movement through center
Heat control strategies: preventing burn-through while ensuring adequate fusion
Vertical fillet welds: building consistent leg size throughout weld length
Critical applications: high-rise construction in Saudi Arabia and UAE skyscrapers
Extensive practice: 3G butt joint welding on structural steel plates
Performance testing: bend test specimen preparation for ductility verification
Learning Outcomes: Mastery of horizontal and vertical welding positions essential for 70% of welding applications in GCC construction and African infrastructure projects.
Day 4: Overhead Welding and Pipe Welding Fundamentals
Morning Session: Overhead Position (4G/4F) Welding
Overhead welding challenges: molten metal control, slag management, safety concerns
Body positioning and ergonomics: minimizing fatigue during overhead operations
Electrode size selection: typically smaller diameter (2.5mm-3.2mm) for better control
Current reduction: 10-15% lower amperage preventing excessive droplet size
Short arc technique: tight arc length preventing large molten pool formation
Stringer beads preference: narrow beads reducing slag trapping risk
Overhead fillet welds: critical for structural connections and underside repairs
Applications: tank bottom repairs, overhead piping, bridge understructures
Practical exercises: 4G groove weld qualification on carbon steel test plates
Welding overhead safely: preventing hot metal and slag from falling on welder
Afternoon Session: Pipe Welding Introduction (5G Position)
Pipe welding importance in GCC oil and gas infrastructure and African pipelines
Pipe joint preparation: beveling, land thickness, root opening requirements
Root pass techniques: E6010 open root keyhole method for complete penetration
Fixed pipe (5G) welding sequence: 12 o’clock to 6 o’clock, alternating sides
Hot pass application: E6010/E6011 fast travel speed removing slag and oxidation
Fill and cap passes: E7018 low-hydrogen electrodes for structural integrity
API 1104 qualification requirements for pipeline construction certification
Pipeline welding career opportunities: Saudi Aramco projects, African gas pipelines
Hands-on practice: 5G position on 4-inch schedule 40 carbon steel pipe
Visual inspection criteria: uniform bead profile, proper reinforcement, no defects
Learning Outcomes: Complete all-position welding capability and introduction to high-demand pipe welding skills for GCC petrochemical and African energy sector employment.
Day 5: Welding Qualification Testing and Career Development
Morning Session: AWS and ASME Qualification Testing
Welding Procedure Specification (WPS): understanding essential variables
Performance Qualification Test (PQT): test plate/pipe setup and execution
Welder qualification ranges: thickness, diameter, position qualified by single test
Bend test procedures: guided bend test fixture, acceptance criteria
Visual examination standards: undercut limits, porosity size, crack prohibition
Radiographic testing basics: understanding RT film interpretation for welds
Qualification documentation: welder performance qualification (WPQ) records
Requalification requirements: 6-month activity rule, code changes, essential variable changes
Mock qualification test: simulated AWS D1.1 3G test plate welding and evaluation
International certifications: CSWIP, CWB, TÜV recognition across global markets
Afternoon Session: Advanced Applications and Career Pathways
Specialized SMAW applications: cast iron repair, hard surfacing, dissimilar metals
Welding in extreme conditions: high winds (desert), high humidity (coastal GCC)
Maintenance and repair welding: equipment breakdown response in African mining
Welding job market analysis: salary expectations in KSA (SAR 4,000-12,000/month)
Career progression paths: welder → lead welder → welding inspector → welding supervisor
Entrepreneurship opportunities: starting mobile welding services in Oman and Africa
Continuing education: TIG welding, MIG welding, pipe welding specialization courses
Employer requirements: Saudi Aramco approved welder list, ADNOC contractor qualification
Job placement assistance: connections with GCC fabrication companies and African contractors
Final practical assessment and course certification ceremony
Learning Outcomes: Job-ready SMAW welding skills with clear understanding of qualification requirements and career opportunities in booming GCC and African industrial markets.
Course Benefits for GCC and African Markets
✓ 90% hands-on training with industrial-grade equipment used in KSA and UAE facilities
✓ AWS D1.1 qualification test preparation for immediate employment eligibility
✓ All-position welding competency (1G through 5G) for versatile job applications
✓ Bilingual instruction (English/Arabic) for accessibility across Middle East
✓ Job placement assistance with leading contractors in Saudi Arabia, Oman, Qatar
✓ Industry-recognized certification accepted across GCC countries and African markets
✓ Small class sizes (maximum 8 students per instructor) ensuring personalized attention
✓ Lifetime technical support and refresher training opportunities
Investment in High-Demand Skills
Arc stick welding remains the most versatile and widely used welding process across Saudi Arabia’s construction boom, Oman’s infrastructure development, UAE’s industrial expansion, and Africa’s rapid industrialization. With Vision 2030 megaprojects in KSA and massive infrastructure investments across Africa, demand for certified SMAW welders has never been higher. Graduates earn competitive salaries and enjoy excellent job security in oil and gas, construction, shipyards, power plants, and manufacturing facilities.
Enroll today to master the most essential welding skill and launch your career in the thriving GCC and African industrial sectors!
Keywords: stick welding course KSA, SMAW training Saudi Arabia, arc welding certification Oman, stick welding jobs GCC, arc welder training Africa, AWS welding qualification Middle East, E7018 electrode training, pipe welding course Gulf, structural welding certification, Saudi Aramco welder qualification, ADNOC welding jobs, stick welding training UAE, certified welder Africa, welding courses Qatar Kuwait Bahrain, pipeline welding career, SMAW certification program


